人工内耳 is an implantable hearing aid device which provides a sense of sound to the person with severe to profound sensorineural hearing loss.は、重度から重度の感音難聴の人に音の感覚を提供する埋め込み型補聴器です。 Unlike the traditional deaf-aid, the working principle of cochlear implant is not amplifying the sound but apply electrical stimulation to the well-functioning auditory nerve in the cochlea.従来の補聴器とは異なり、人工内耳の動作原理は音を増幅することではなく、蝸牛内の十分に機能している聴覚神経に電気刺激を加えることです。
聴覚系はどのように機能しますか?

- 人間の耳は、外耳、中耳、内耳に分けることができます。
- Outer ear includes auricle and canal.外耳には耳介と運河が含まれます。 Sound will further transmit through the canal after collecting and filtered by auricle.音は、耳介によって収集およびフィルタリングされた後、運河を通ってさらに伝達されます。
- Middle ear includes the tympanic membrane and Ossicular chain.中耳には鼓膜と耳小骨鎖が含まれます。 The tympanic membrane will vibrate in path with sound rhythm.鼓膜は音のリズムで経路内で振動します。 The sound will translate to mechanical vibration during this process and vibration will be further entered the inner ear via Ossicular chain.この過程で音は機械的振動に変換され、振動は耳小骨チェーンを介して内耳にさらに入ります。
- Inner ear includes the cochlea and auditory nerve.内耳には蝸牛神経と聴覚神経が含まれます。 The sound vibration will lead to the movement of cochlear fluid and thus cause the bends of hair cells.音の振動は蝸牛液の動きにつながり、有毛細胞の曲がりを引き起こします。 The neutral signal generated by hair cell will be picked up by the auditory nerve.有毛細胞によって生成された中性信号は、聴覚神経によって拾われます。 Therefore, the signal will be translated into sound by the brain.したがって、信号は脳によって音に変換されます。
人工内耳の構造
- 人工内耳システムには、内部部分と外部部分が含まれています。
- Internal part of cochlear implant includes receiver, decoder, and stimulator.人工内耳の内部には、レシーバー、デコーダー、およびスティミュレーターが含まれます。 Internal part will be placed under the skin behind the ear by surgery.内部は手術により耳の後ろの皮膚の下に配置されます。
- External part includes microphone, speech processor, and transmitter.外部部品には、マイク、音声プロセッサ、送信機が含まれます。 External part is always placed behind the ear.外部部品は常に耳の後ろに配置されます。

人工内耳の動作原理
Hair cells of the deaf person are damaged or reduced due to different lesions, then residues cannot drive auditory nerve normally.聴覚障害者の有毛細胞は、さまざまな病変のために損傷または減少し、残留物は聴覚神経を正常に駆動できません。 For cochlear implant, the electrical stimulation will apply to the auditory nerve directly which skip to the sector of hair cells.人工内耳の場合、電気刺激は聴覚神経に直接適用され、有毛細胞のセクターにスキップします。
- マイクは音声を収集し、情報は音声プロセッサに広がります。
- 音声プロセッサは、情報をデジタル化し、フィルタリングし、コード化します。
- デジタル信号は、ワイヤーを介して送信コイルに伝播し、皮膚の下の受信機および刺激装置に信号を送信する。
- 受信機と刺激装置のデコード情報。
- 電子信号は、電極アレイの位置を指定するために渡され、したがって、蝸牛の神経線維を刺激します。
- 電子信号は、神経が電子信号を受信した後、脳によって音として認識されます。
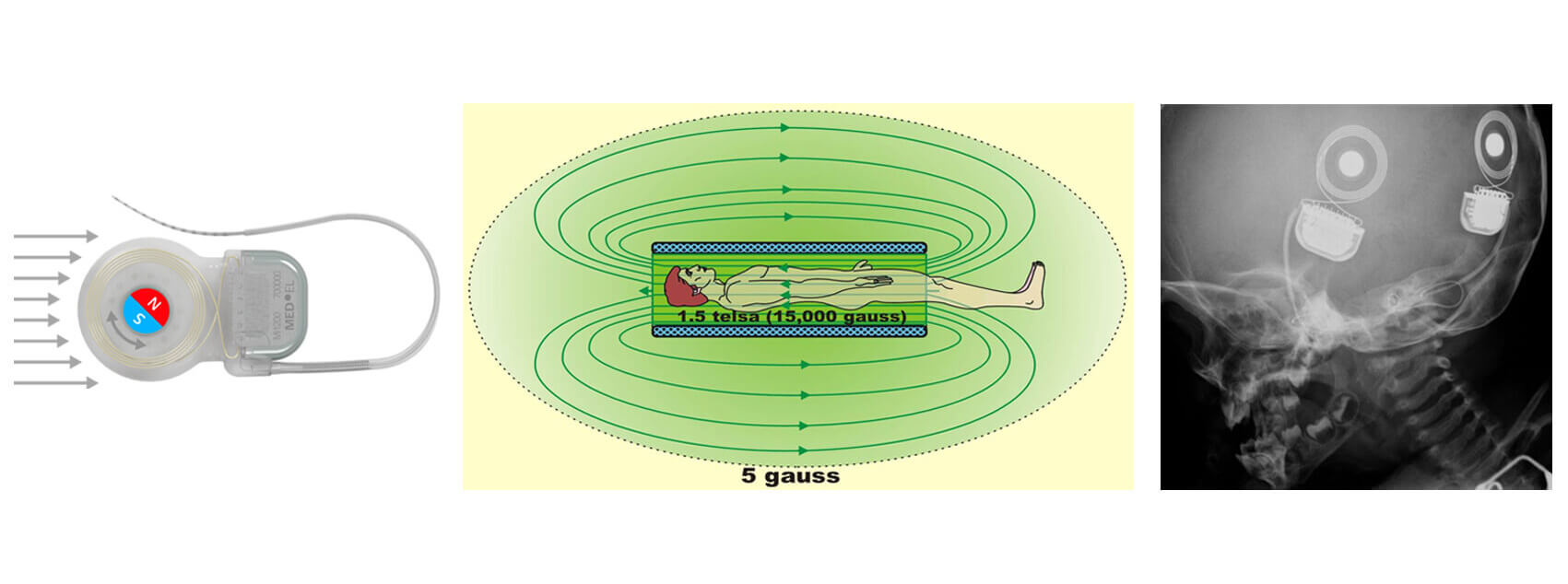
MRI互換の人工内耳磁石
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is a common medical imaging procedure nowadays, and detailed images of internal organs and tissue can be got relied on the powerful magnetic field which generated by MRI.磁気共鳴画像法(MRI)は、今日の一般的な医用画像法であり、内臓や組織の詳細な画像は、MRIによって生成される強力な磁場に依存することができます。 For cochlear implant system, the processor magnet attracts to the internal part's magnet to hold it in place.人工内耳システムの場合、プロセッサの磁石が内部部品の磁石に引き付けられ、所定の位置に保持されます。 Therefore, MRI becomes an extremely important issue for cochlear implant users.したがって、MRIは人工内耳のユーザーにとって非常に重要な問題になります。 The significant risk of complications will be carried during MRI, such as pain, discomfort, and痛み、不快感、およびなどの合併症の重大なリスクは、MRI中に運ばれます マグネット's dislocation.の脱臼。 Cochlear implant manufacturers have introduced many solutions to solve disadvantage influence of the powerful magnetic field (1.5T and 3.0T) to internal cochlear implant magnets.人工内耳メーカーは、内部の人工内耳磁石に対する強力な磁場(XNUMXTおよびXNUMXT)の悪影響を解決するために多くのソリューションを導入しています。 In fact, how to make self-aligning cochlear implant magnets to avert surgery is still mainstream manufacturers.実際、手術を回避するために自動調心人工内耳磁石を作成する方法は、依然として主流のメーカーです。 Magnets with special magnetization direction and isotropic NdFeB powder has been already used currently.特殊な磁化方向と等方性のNdFeB粉末を備えた磁石は、現在すでに使用されています。